Difference between revisions of "Time Course"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| Line 17: | Line 17: | ||
|} | |} | ||
==2022.06.31== | ==2022.06.31== | ||
| − | + | <htmltag tagname="img" src="https://wiki.laviebay.hkust.edu.hk/deLemus/RESEARCH_TEAMS/images/PublishedPlot/30.png" alt="test for htmltag img" class="wikimg" style="display: block;width:100%;margin-left: auto;margin-right: auto;"></htmltag> | |
| + | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | ! Outlined Mutations !! Confirmed in VOC/Emerging Variants | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | F157L || BQ.1 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | G257S || BQ.1 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | G339H || BQ.1 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | N460K || BQ.1 | ||
| + | |} | ||
<!-- | <!-- | ||
===F486P/I === | ===F486P/I === | ||
Revision as of 17:49, 13 February 2023
TBA
Previously Confirmed Mutations
In the last 6 months, 3 new members of the omicron (B.1.1.529) lineage have emerged, and subsequently been recognized as variants of interest (VOI) by the World Health Organization (WHO), which are the BA.2.75, XBB, and BQ.1 subvariants that rose to prominence in July, August and October 2022 respectively. Each of these VOIs has brought along an array of novel mutable sites crucial for refining the viral fitness of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). Leading mutations identified by our deLemus analysis that emerged within the aforementioned timeframe are listed as follows:
2022.08.31
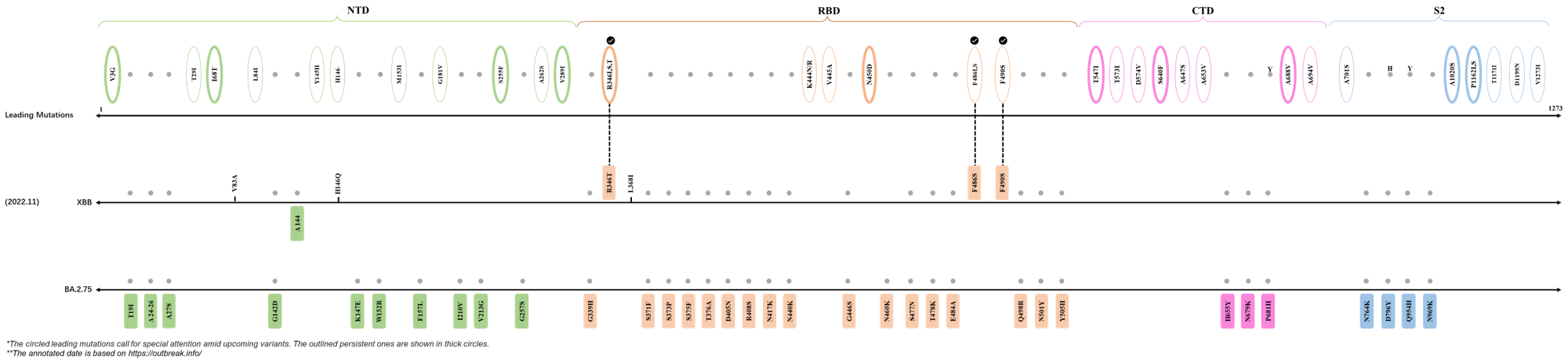
| Outlined Mutations | Confirmed in VOC/Emerging Variants |
|---|---|
| R346T | XBB |
| F486S | XBB |
| F490S | XBB |
2022.06.31

| Outlined Mutations | Confirmed in VOC/Emerging Variants |
|---|---|
| F157L | BQ.1 |
| G257S | BQ.1 |
| G339H | BQ.1 |
| N460K | BQ.1 |