deLemus
Dynamic Expedition of Leading Mutations in SARS-CoV-2 Spike Glycoproteins
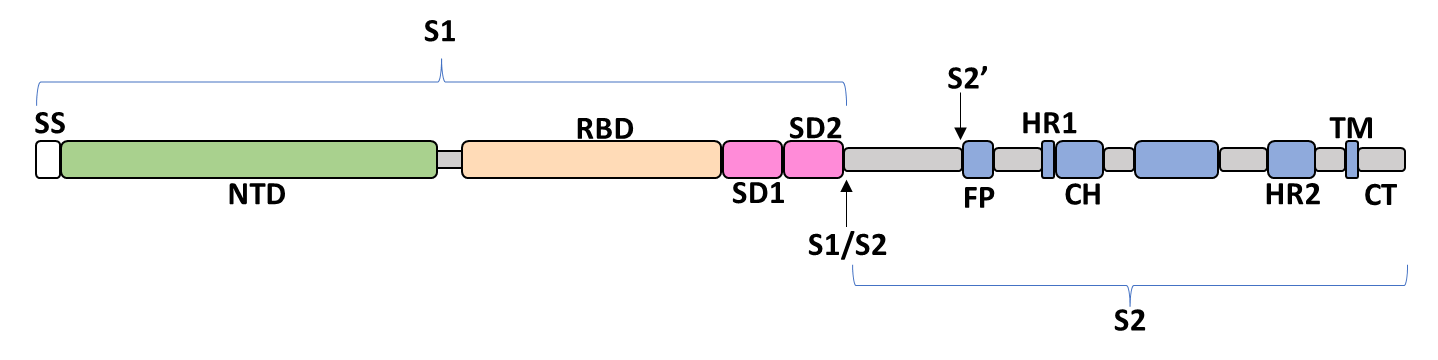
Spike Glycoprotein
The spike glycoprotein of SARS-CoV-2 is a trimeric type I viral fusion protein that binds the virus to the angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) receptor of a host cell.[1] It is composed of 2 subunits: the N-terminal subunit 1 (S1) and C-terminal subunit 2 (S2), within which multiple domains lie. The S1 region facilitates ACE2 binding and is made up of an N-terminal domain (NTD), a receptor-binding domain (RBD), and 2 C-terminal subdomains (CTD1 and CTD2), while the downstream S2 region is responsible for mediating virus-host cell membrane fusion.
Update
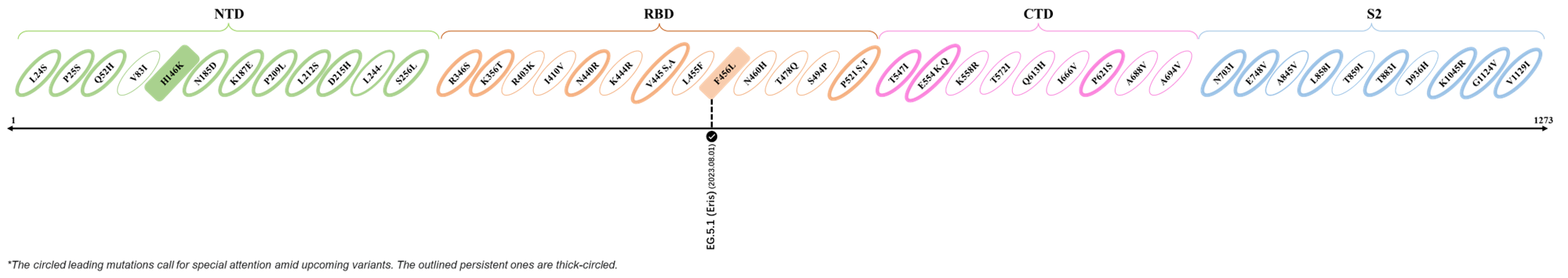
The identified leading mutations in 2023 are listed as follows [2]:
- Generated 3D structure of spike protein with highlighted leading mutations (AlphaFold2, colab version 2022).
Here are the recently confirmed leading mutations.
2023.08.04 - 2023.08.22
| Outlined Mutations | Confirmed in VOC/Emerging Variants |
|---|---|
| N185D | XBB.1.5 |
| L212S | FY.4.2 |
| V445A | XBC.1.6 |
| L455F | EG.5.1.1 |
| F456L | EG.5.1 (Eris) |
| E554Q | XBB.1.5.18 |
| Q613H | XBB.1.16 |
| T883I | XBB.1.16 |
*The reported mutations of detected variants are from Cov-Lineages[3]
- Generated 3D structure of spike protein with highlighted leading mutations (AlphaFold2, colab version 2022).
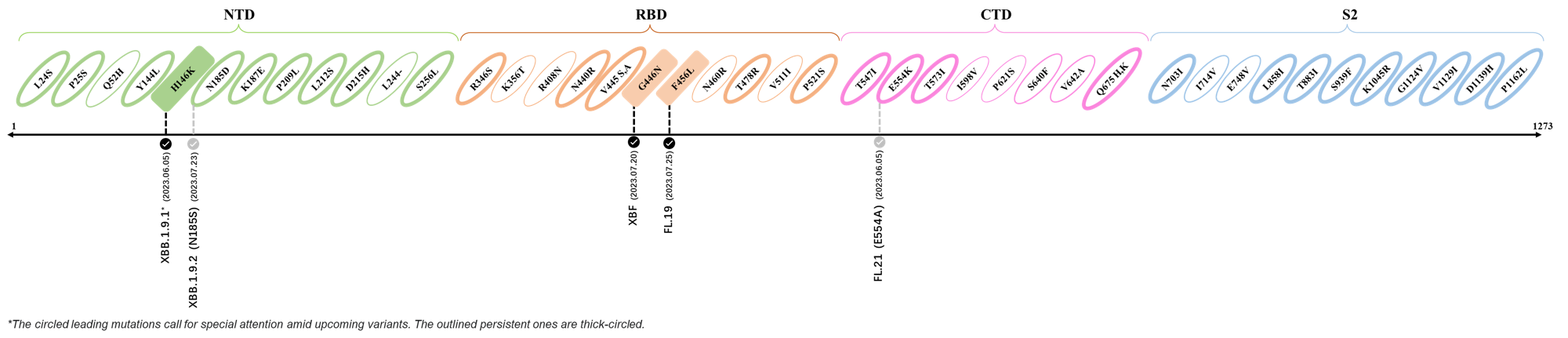
Here are the recently confirmed leading mutations.
2023.06.30 - 2023.07.05
| Outlined Mutations | Confirmed in VOC/Emerging Variants |
|---|---|
| H146K | FL.2.3 (XBB.1.9.1.2.3) |
| S446N | FL.19 |
| F456L | XBF |

- Generated 3D structure of spike protein with highlighted leading mutations (AlphaFold2, colab version 2022).
Here are the recently confirmed leading mutations.
2023.06.01 - 2023.06.13
| Outlined Mutations | Confirmed in VOC/Emerging Variants |
|---|---|
| F490P | XBB.1.9.1 |
| E554K | XBB.1.9.1 (sublineage) |
| Q675K | XBB.1.22.1 |
| L858I | CH.1.1.1 |

- Generated 3D structure of spike protein with highlighted leading mutations (AlphaFold2, colab version 2022).
Here are the recently confirmed leading mutations.
2023.05.01 - 2023.05.12
| Outlined Mutations | Confirmed in VOC/Emerging Variants |
|---|---|
| F456L | FD.1.1 & EG.5.1 (2023.08) |
| S494P | XBB.2.3 & XBB.1.1 |
| T572I | FY.1 ( XBB.1.22.1.1 ) |
*The reported mutations of detected variants are from GISAID

- Generated 3D structure of spike protein with highlighted leading mutations (AlphaFold2, colab version 2022).
Here are the recently confirmed leading mutations.
2023.04.01 - 2023.04.21
| Outlined Mutations | Confirmed in VOC/Emerging Variants |
|---|---|
| H146K | XBB.1.5 & XBB.1.16 |
| M153I | XBB.2.3.3 |
| E180V | XBB.1.16 |
| K444R | XBB.1.5 |
| T478R | XBB.1.16, XBB.1.5, CH.1.1.2 & XBB.2.3 |
| F490P | XBB.2.6 |
| S494P | XBB.1.5 |
| Q613H | XBB.1.16 |
| P621S | XBB.2.3 |
| A688V | XAY.1.1.1 |
- Generated 3D structure of spike protein with highlighted leading mutations (AlphaFold2, colab version 2022).
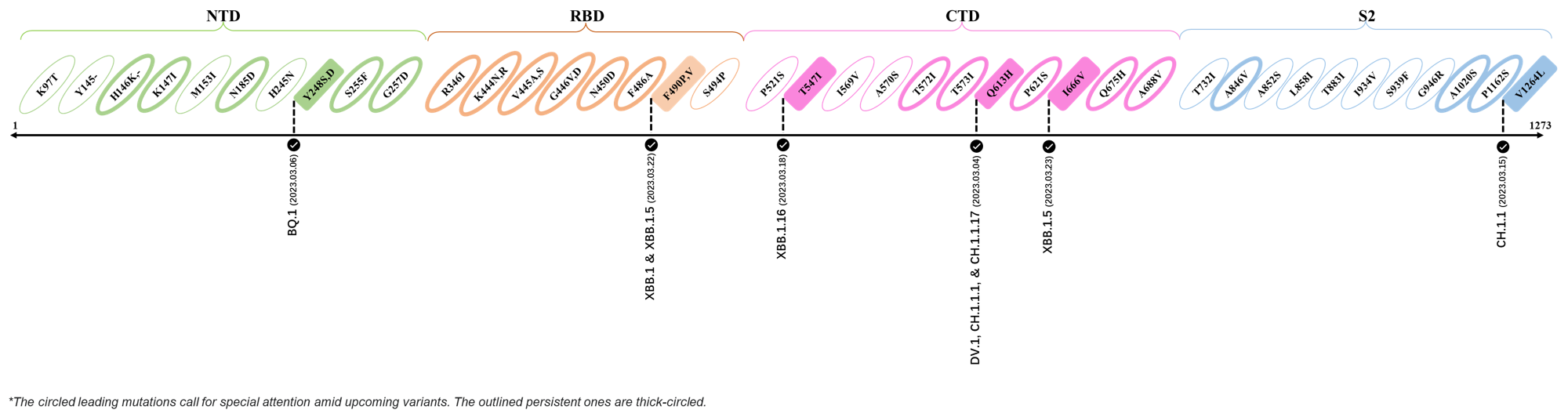
Here are the recently confirmed leading mutations.
2023.03.01 - 2023.03.21
| Outlined Mutations | Confirmed in VOC/Emerging Variants |
|---|---|
| Y248S | BQ.1 |
| F490P | XBB.1 & XBB.1.5 |
| T547I | XBB.1.16 |
| Q613H | DV.1, CH.1.1.1 & CH.1.1.17 |
| I666V | XBB.1.5 |
| V1264L | CH.1.1 |
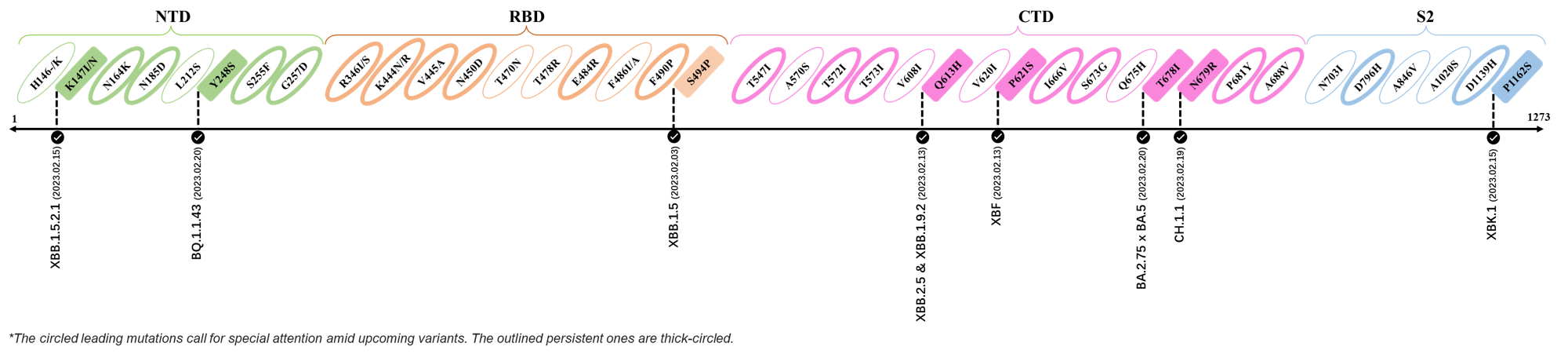
- Generated 3D structure of spike protein with highlighted leading mutations (AlphaFold2, colab version 2022).
Here are the recently confirmed leading mutations.
2023.02.03 - 2023.02.20
| Outlined Mutations | Confirmed in VOC/Emerging Variants |
|---|---|
| K147I | XBB.1.5.2.1 |
| Y248S | BQ.1.1.43 |
| S494P | XBB.1.5 |
| Q613H | XBB.1.9.2 & XBB.2.4 |
| P612S | XBF |
| T678I | BA.2.75 x BA.5 |
| N679R | CH.1.1 |
| P1162S | XBK.1 |
*The reported mutations of detected variants are from GISAID[4]
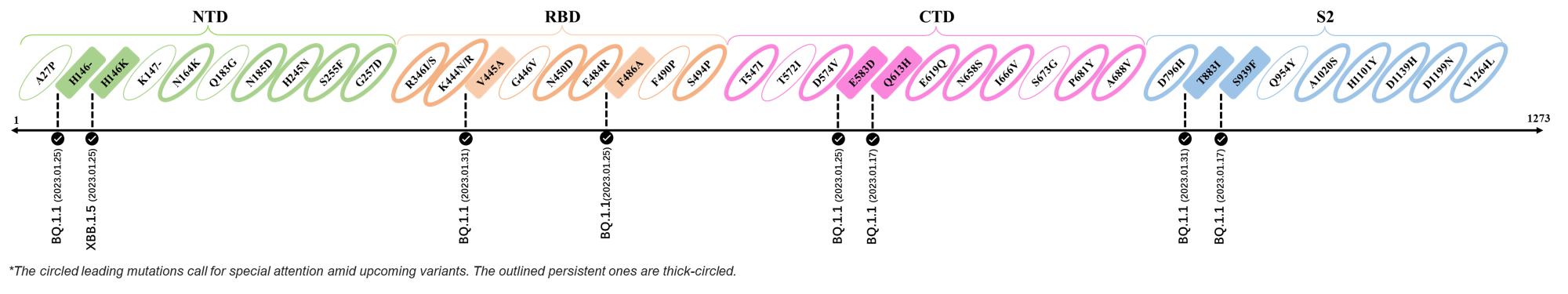
- Generated 3D structure of spike protein with highlighted leading mutations (AlphaFold2, colab version 2022).
Here are the recently confirmed leading mutations.
2023.01.31
| Outlined Mutations | Confirmed in VOC/Emerging Variants |
|---|---|
| V445A | BQ.1.1 |
| T883I | BQ.1.1 |
2023.01.17 - 2023.01.25
| Outlined Mutations | Confirmed in VOC/Emerging Variants |
|---|---|
| H146- / H146K | BQ.1.1 / XBB.1.5 |
| F486A | BQ.1.1 |
| E583D | BQ.1.1 |
| Q613H | BQ.1.1 |
| S939F | BQ.1.1 |
References
- ↑ Jackson, C. B., Farzan, M., Chen, B. & Choe, H. Mechanisms of SARS-CoV-2 entry into cells. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 23, 3 (2021).
- ↑ deLemus team, Analysis of Leading Mutations in SARS-CoV-2 Spike Glycoproteins (in preparation, 2023).
- ↑ Cov-Lineages https://cov-lineages.org/
- ↑ GISAID https://gisaid.org/
Cite error: <ref> tag with name "Del Rio" defined in <references> is not used in prior text.
Cite error: <ref> tag with name "European Centre" defined in <references> is not used in prior text.
Cite error: <ref> tag with name "Karim" defined in <references> is not used in prior text.
Cite error: <ref> tag with name "Wang" defined in <references> is not used in prior text.
